How ChatGPT Works: Simple Explanation for Beginners
Ever wondered what happens behind the scenes when you type a question into ChatGPT and get an instant, intelligent response? You're not alone. ChatGPT has revolutionized how millions interact with AI, yet most users don't understand how it actually works. This beginner-friendly guide breaks down ChatGPT's technical architecture—from transformer models to training processes—without requiring a computer science degree.
Understanding how ChatGPT works helps you use it more effectively, recognize its limitations, and make informed decisions about AI tools. Whether you're a curious beginner or a professional looking to leverage AI productivity tools like ChatGPT Toolbox for organizing conversations, exporting chats, and searching history, this guide gives you the foundational knowledge you need.
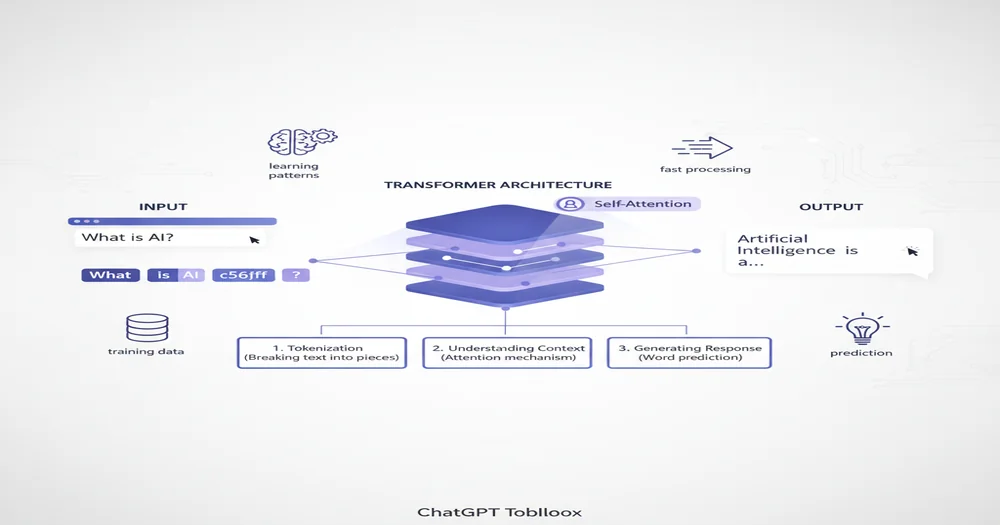
What Is ChatGPT? A Simple Overview
ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is an AI language model developed by OpenAI that can understand and generate human-like text. Think of it as a highly sophisticated autocomplete system—but instead of just suggesting the next word in a text message, it can write entire essays, answer complex questions, write code, and engage in natural conversations.
At its core, ChatGPT is built on a technology called a transformer, which is a type of neural network architecture specifically designed for processing and generating text. According to OpenAI's ChatGPT documentation, the model has been trained on hundreds of billions of words from books, websites, and other text sources to learn patterns in human language.
Key Characteristics of ChatGPT
- Conversational: Maintains context across multiple messages in a conversation
- Generative: Creates original text rather than just retrieving pre-written answers
- Pre-trained: Already learned from massive amounts of text before you ever interact with it
- Transformer-based: Uses attention mechanisms to understand relationships between words
Unlike traditional search engines that find and display existing content, ChatGPT generates new responses based on patterns it learned during training. This makes it incredibly versatile but also means it can sometimes produce incorrect or "hallucinated" information—a limitation we'll explore later.
The Transformer Architecture: ChatGPT's Brain
The transformer architecture, first introduced by Google researchers in their 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need," revolutionized natural language processing. According to transformer architecture research, this innovation made ChatGPT and other large language models possible by solving critical problems in how AI processes text.
What Is a Transformer? (Simple Explanation)
Imagine you're reading a sentence: "The bank was steep, so we couldn't climb it." To understand what "bank" means (river bank, not financial bank), you need to look at the surrounding words—"steep" and "climb" provide context. This is exactly what transformers do, but at massive scale across entire documents.
A transformer is a neural network that can pay attention to different parts of the input text to understand context and meaning. Unlike older AI models that read text sequentially (word by word), transformers can process all words simultaneously while understanding their relationships.
How ChatGPT Uses the Decoder-Only Transformer
According to decoder-only transformer research, ChatGPT uses a specialized version called a "decoder-only" architecture. Here's what that means in simple terms:
| Component | What It Does | Simple Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Input Layer | Converts your text into numbers (tokens) the model can process | Like translating English into a language the computer understands |
| Self-Attention Mechanism | Identifies which words in the input are most relevant to each other | Like highlighting key phrases in a document to understand meaning |
| Masked Attention | Ensures the model only looks at previous words when predicting the next one | Like covering up the rest of a sentence while you're writing it word by word |
| Feed-Forward Neural Networks | Processes the attention output to generate predictions | Like your brain combining clues to figure out what comes next |
| Output Layer | Converts predictions back into readable text | Like translating the computer's thoughts back into English |
The Self-Attention Mechanism Explained
Self-attention is the "secret sauce" that makes transformers so powerful. According to DataCamp's transformer guide, this mechanism allows ChatGPT to understand context by calculating "attention scores" that measure how much each word should influence the understanding of every other word.
Example: In the sentence "The animal didn't cross the street because it was too tired," the word "it" needs high attention to "animal" (not "street") to understand the pronoun reference. ChatGPT's attention mechanism automatically figures this out.
How ChatGPT Is Trained: The Three-Stage Process
ChatGPT doesn't magically know how to have conversations. It goes through a comprehensive three-stage training process that takes months and costs millions of dollars. According to OpenAI's instruction-following documentation, this training process is what transforms a basic language model into an AI assistant.
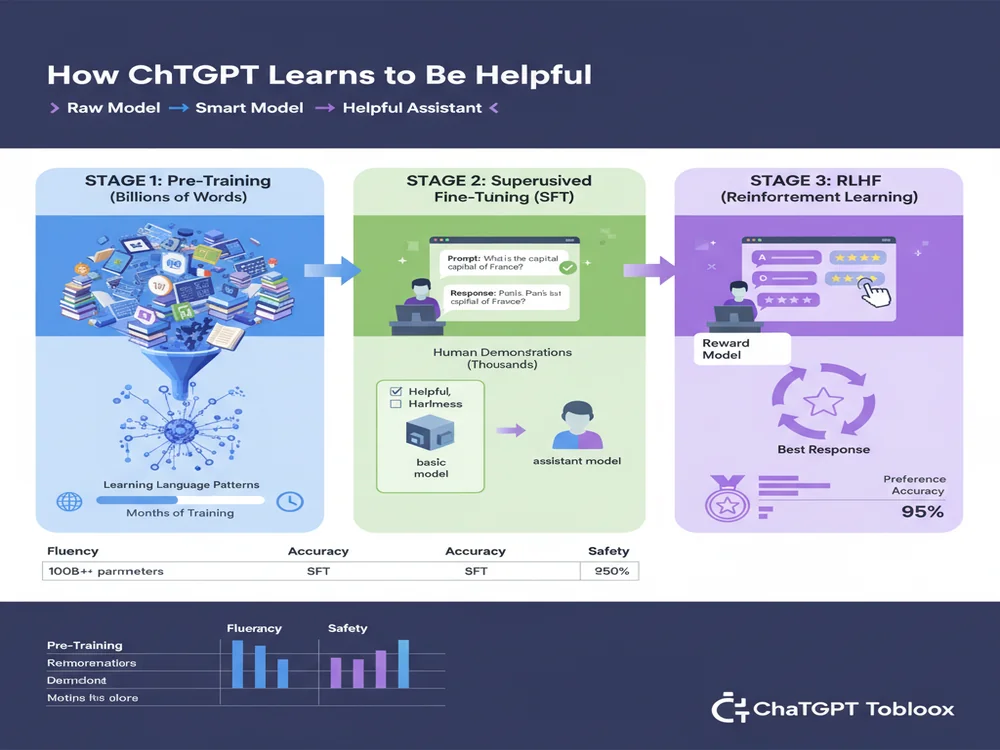
Stage 1: Pre-Training (Learning from the Internet)
In the first stage, ChatGPT reads massive amounts of text from the internet—books, articles, websites, Wikipedia, GitHub code, and more. According to research on how ChatGPT actually works, models like GPT-4 are trained on hundreds of billions of words.
What the model learns:
- Language patterns: Grammar, syntax, and how words typically appear together
- World knowledge: Facts, concepts, and relationships between ideas
- Reasoning patterns: How arguments are structured and conclusions are drawn
- Code syntax: Programming languages and how code works
During pre-training, the model plays a simple but powerful game: predict the next word. Given a sequence like "The cat sat on the...", the model tries to predict "mat" or "chair." It does this billions of times, gradually learning to understand and generate coherent text.
Training cost: Pre-training GPT-4 reportedly cost over $100 million in computing resources and took several months on thousands of high-powered GPUs.
Stage 2: Supervised Fine-Tuning (Learning from Human Demonstrations)
After pre-training, the model knows a lot about language but doesn't yet know how to be a helpful AI assistant. In stage two, human trainers demonstrate desired behavior by writing example conversations.
How it works:
- Human labelers are given various prompts (e.g., "Explain photosynthesis to a 5-year-old")
- Trainers write ideal responses showing how ChatGPT should answer
- The model learns from these examples through supervised learning
- Thousands of demonstration conversations teach the model to be helpful, harmless, and honest
This creates what's called the Supervised Fine-Tuned (SFT) model—a baseline version that understands it's supposed to answer questions and assist users.
Stage 3: RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback)
The final stage is where ChatGPT becomes truly intelligent at choosing the best responses. According to Hugging Face's RLHF guide and reinforcement learning research, RLHF is what makes ChatGPT produce desirable, non-toxic, and factual outputs.
How RLHF works (simplified):
- The model generates multiple responses to the same prompt
- Human raters rank the responses from best to worst based on quality, helpfulness, and safety
- A "reward model" learns to predict which responses humans prefer
- The model is retrained using reinforcement learning to maximize the predicted reward
Think of RLHF like training a dog: instead of just showing the dog what to do (supervised learning), you also give rewards when it does well and corrections when it doesn't. Over thousands of iterations, the model learns to produce responses that humans consistently rate as high-quality.
According to RLHF research, this training approach led ChatGPT to produce more helpful, accurate, and safer responses compared to models trained only with supervised learning.
How ChatGPT Generates Responses
Now that you understand ChatGPT's architecture and training, let's walk through exactly what happens when you type a message and hit enter.
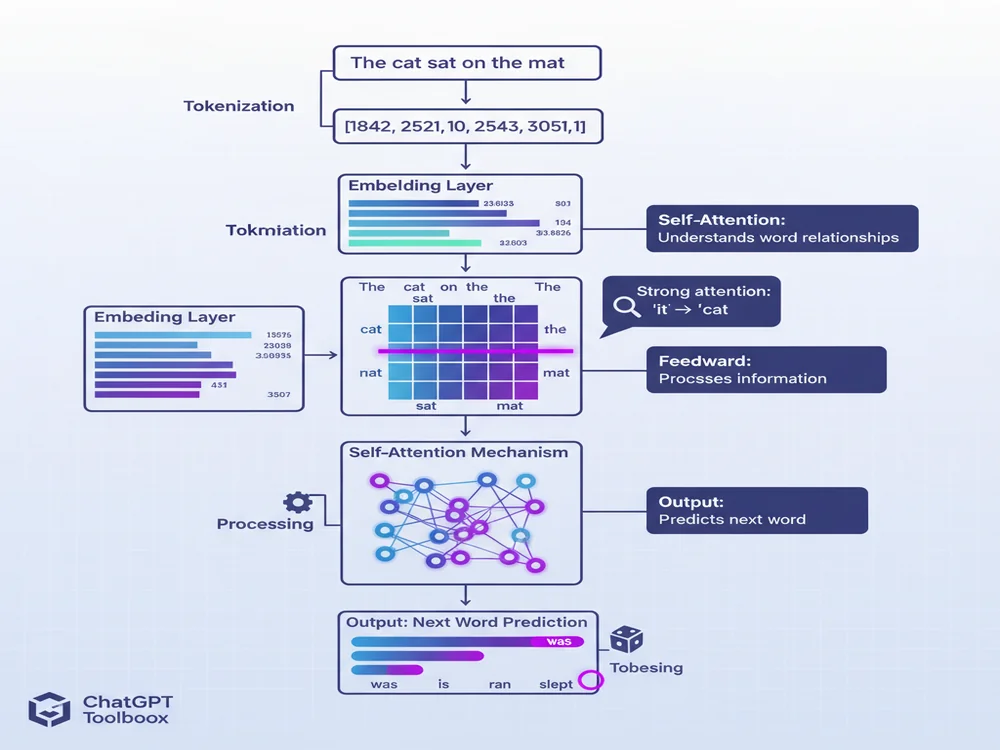
The Response Generation Process (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Tokenization
Your input text is broken into smaller pieces called "tokens." According to transformer architecture guides, tokens can be words, parts of words, or even individual characters. For example, "ChatGPT is amazing" might become ["Chat", "G", "PT", " is", " amazing"].
Step 2: Embedding
Each token is converted into a vector (a list of numbers) that represents its meaning in mathematical space. Words with similar meanings have similar vectors.
Step 3: Positional Encoding
Since transformers process all tokens simultaneously, the model adds positional information so it knows the order of words. This ensures "dog bites man" is understood differently from "man bites dog."
Step 4: Attention Calculation
The self-attention mechanism calculates how much each word should "attend to" every other word, building a deep understanding of context and relationships.
Step 5: Prediction
The model predicts the next token based on all previous context. It generates a probability distribution over thousands of possible tokens (e.g., "The" might have 15% probability, "A" might have 12%, etc.).
Step 6: Sampling
The model selects a token based on these probabilities (with some randomness controlled by "temperature" settings). This selected token becomes part of the response.
Step 7: Iteration
Steps 5-6 repeat, with the model predicting one token at a time, until it generates a special "end of response" token or reaches a maximum length.
This entire process happens in milliseconds, which is why ChatGPT can produce long, coherent responses almost instantly. According to Zapier's ChatGPT guide, this autoregressive generation approach (predicting one token at a time based on previous tokens) is fundamental to how all large language models work.
Understanding ChatGPT's Limitations
ChatGPT is powerful, but it's not perfect. Understanding its limitations helps you use it more effectively and avoid common pitfalls. According to MIT's research on ChatGPT limitations, awareness of these constraints is essential for responsible AI use.
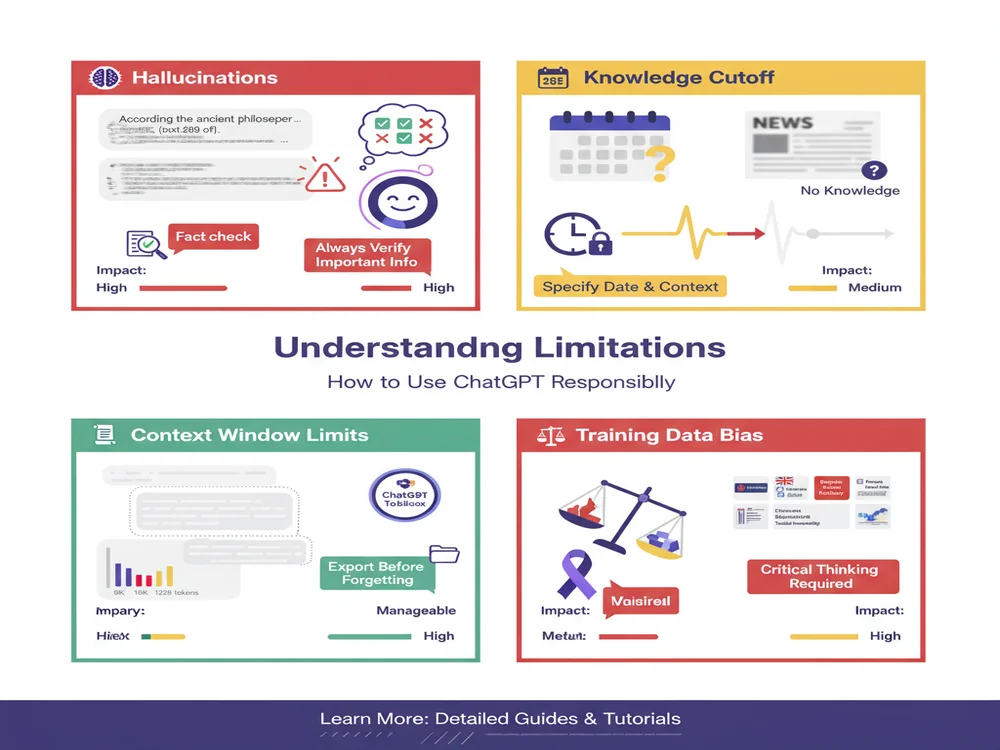
1. Hallucinations (Making Up Information)
ChatGPT sometimes generates false information that sounds convincing. According to 2026 AI hallucination research, this happens because the model is optimized to produce fluent, confident-sounding text—not guaranteed accurate answers.
Why hallucinations happen:
- The model doesn't "know" it doesn't know: It generates text based on patterns, not factual databases
- Training data gaps: If the model hasn't seen enough information about a topic, it may invent plausible-sounding details
- Fluency over accuracy: The model prioritizes producing coherent text over admitting uncertainty
How to minimize hallucinations:
- Verify important facts with authoritative sources
- Ask ChatGPT to cite sources (though these can also be hallucinated)
- Use specific, detailed prompts rather than vague questions
- Request step-by-step reasoning to catch logical errors
According to 2026 LLM comparison research, newer models like GPT-5.2 feature fewer hallucinations, but no model is completely immune to this problem.
2. Knowledge Cutoff (Outdated Information)
ChatGPT's knowledge is frozen at its training cutoff date. As of 2026, different models have different cutoff dates:
| Model | Knowledge Cutoff | Web Browsing |
|---|---|---|
| GPT-3.5 | January 2022 | No |
| GPT-4o | October 2023 | Yes (with plugins) |
| GPT-4.5 | April 2025 | Yes (built-in) |
| GPT-5 (Fast/Thinking) | December 2025 | Yes (built-in) |
For current events, stock prices, or recent developments, always verify with real-time sources or use models with web browsing capabilities.
3. Context Window Limitations
ChatGPT can only "remember" a limited amount of text at once, measured in tokens. According to MIT's AI education resources, this "context window" acts like the model's short-term memory.
Context window sizes (2026):
- GPT-3.5: 16,000 tokens (~12,000 words)
- GPT-4o: 128,000 tokens (~96,000 words)
- GPT-4.5: 256,000 tokens (~192,000 words)
- GPT-5: 1,000,000+ tokens (~750,000+ words)
When conversations exceed the context window, ChatGPT "forgets" earlier parts. This is where ChatGPT Toolbox becomes invaluable—you can export important conversations, organize them in folders, and search through your entire history to find relevant information from past chats.
4. Training Data Biases
Because ChatGPT learns from internet text, it can inherit biases present in that training data. According to research on AI bias, these biases can appear in multiple ways:
- Gender stereotypes: Associating certain professions with specific genders
- Cultural biases: Favoring Western perspectives or English-language content
- Representation gaps: Better performance on topics well-represented in training data
- Political leanings: Reflecting viewpoints common in training sources
OpenAI continues working to reduce these biases through improved training techniques and human feedback, but users should remain aware that perfect neutrality is currently impossible.
5. Can't Execute Real Actions
ChatGPT can explain how to do things but can't actually execute them. It can't:
- Send emails or make phone calls
- Access your files or personal data (unless you explicitly share them)
- Browse the web in real-time (except in specific browsing mode)
- Run code on your computer (except in Code Interpreter mode)
- Remember conversations across different chat sessions (unless using Memory feature)
Technical Specs: ChatGPT Model Comparison (2026)
Different ChatGPT models have different capabilities and limitations. Here's a comprehensive comparison for 2026:
| Specification | GPT-3.5 | GPT-4o | GPT-4.5 | GPT-5 (Fast) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 175 billion | ~1 trillion | ~1.5 trillion | ~2.5 trillion |
| Context Window | 16K tokens | 128K tokens | 256K tokens | 1M+ tokens |
| Training Data Cutoff | Jan 2022 | Oct 2023 | Apr 2025 | Dec 2025 |
| Response Speed | 2-5 seconds | 5-10 seconds | 8-15 seconds | 15-25 seconds |
| Accuracy | Good | Excellent | Outstanding | Near-Perfect |
| Multimodal (Images) | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Availability | Free + Plus | Plus only | Plus + Team | Plus + Team |
For a deeper dive into model differences, check out our comprehensive guide on ChatGPT models explained.
Practical Tips for Using ChatGPT Effectively
Now that you understand how ChatGPT works, here are practical tips to get the best results:
1. Write Clear, Specific Prompts
Instead of: "Tell me about marketing"
Try: "Explain email marketing best practices for B2B SaaS companies in 2026, including specific metrics to track and tools to use"
2. Provide Context and Examples
ChatGPT performs better when you give it context:
- Your role or background
- The desired format (bullet points, essay, code, etc.)
- The audience for the output
- Examples of what you want
3. Use Multi-Step Prompts for Complex Tasks
Break complex requests into steps:
- "First, outline the main sections of a blog post about AI"
- "Now write a detailed introduction for the first section"
- "Add three specific examples with data to support this point"
For managing complex prompt workflows, use ChatGPT Toolbox's prompt library to save and organize your best prompts with the // shortcut.
4. Fact-Check Important Information
Always verify:
- Statistics and data points
- Historical facts
- Medical or legal advice
- Technical specifications
- Recent news or events
5. Organize Your Conversations
As you accumulate dozens or hundreds of ChatGPT conversations, organization becomes critical. ChatGPT Toolbox helps you:
- Search your entire history: Find any conversation instantly with advanced search features
- Organize with folders: Create custom folder structures for projects, topics, or clients
- Export for backup:Bulk export conversations to TXT, JSON, or Markdown
- Pin important chats: Keep your most valuable conversations easily accessible
Learn more in our guide on how to organize ChatGPT conversations.
The Future of ChatGPT Technology
Understanding how ChatGPT works today helps you anticipate where the technology is heading. According to OpenAI's release notes, several trends are shaping the future:
Larger Context Windows
Future models will handle millions of tokens, allowing you to provide entire books as context or maintain ultra-long conversations without forgetting earlier details.
Multimodal Capabilities
ChatGPT is evolving beyond text to seamlessly handle images, audio, video, and code. GPT-4.5 and GPT-5 already demonstrate sophisticated image understanding and generation.
Reduced Hallucinations
Ongoing research into retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and fact-checking mechanisms is making responses more reliable and grounded in verifiable sources.
Personalization
Future versions will better remember your preferences, work style, and past interactions, creating truly personalized AI assistants that learn from every conversation.
Real-Time Information
Integration with search engines and real-time data sources will eliminate knowledge cutoff limitations for current events and dynamic information.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does ChatGPT understand my questions?
ChatGPT uses a transformer neural network with self-attention mechanisms to process your input text. It breaks your question into tokens, converts them to numerical vectors, and uses attention to understand relationships between words and context. The model then generates a response by predicting one token at a time based on patterns learned from training on hundreds of billions of words.
Is ChatGPT actually intelligent or just predicting text?
ChatGPT is fundamentally a sophisticated pattern-matching system that predicts likely text sequences based on training data. While it doesn't "think" like humans, it demonstrates emergent capabilities like reasoning, problem-solving, and creativity that arise from its massive scale and training. Whether this constitutes true intelligence is debated among AI researchers.
Why does ChatGPT sometimes give wrong answers?
ChatGPT can produce incorrect information (hallucinations) because it's optimized for fluent, coherent text generation rather than factual accuracy. It doesn't have access to truth databases, can't verify claims in real-time, and may fill knowledge gaps with plausible-sounding but false information. Training data limitations, biases, and the probabilistic nature of text generation all contribute to occasional errors.
How many parameters does ChatGPT have?
GPT-3.5 has 175 billion parameters, GPT-4o has approximately 1 trillion parameters, GPT-4.5 has around 1.5 trillion, and GPT-5 has approximately 2.5 trillion parameters. Parameters are the adjustable weights in the neural network that the model learns during training. More parameters generally allow for more nuanced understanding and better performance on complex tasks.
Can ChatGPT learn from my conversations?
ChatGPT has a Memory feature that allows it to remember information from your conversations to personalize future responses. However, the base model itself doesn't learn or update from individual user interactions—only OpenAI can retrain the model. Your conversations may be used to improve future versions if you haven't disabled data sharing in settings.
What is the difference between pre-training and fine-tuning?
Pre-training is the initial phase where ChatGPT learns general language patterns by reading massive amounts of internet text and predicting the next word. Fine-tuning comes after, where the model is trained on specific tasks (like following instructions) using human-written examples and feedback. Pre-training creates general knowledge; fine-tuning specializes the model for particular behaviors.
How does ChatGPT handle multiple languages?
ChatGPT was trained on text in dozens of languages, allowing it to understand and generate responses in multiple languages. The transformer architecture with self-attention works across languages by learning universal patterns in how language functions. However, performance is strongest in English and other well-represented languages in the training data.
What is RLHF and why is it important?
RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) is a training technique where human raters rank multiple ChatGPT responses to the same prompt. The model learns to maximize human preference through reinforcement learning. RLHF is crucial because it teaches ChatGPT to be helpful, harmless, and honest—producing responses that align with human values rather than just grammatically correct text.
Conclusion: Putting Your ChatGPT Knowledge to Work
Understanding how ChatGPT works—from transformer architecture to training processes to response generation—empowers you to use this powerful tool more effectively. You now know that ChatGPT uses self-attention mechanisms to understand context, learns from billions of words during pre-training, and refines its responses through supervised fine-tuning and RLHF.
More importantly, you understand ChatGPT's limitations: hallucinations, knowledge cutoffs, context window constraints, and training data biases. This knowledge helps you use ChatGPT responsibly, verify important information, and recognize when you need alternative sources.
As you continue using ChatGPT for work, learning, or creativity, consider how ChatGPT Toolbox can enhance your experience with features that ChatGPT doesn't offer natively:
- Advanced search: Find any conversation instantly across your entire history
- Folder organization: Create unlimited custom folders and subfolders
- Bulk export: Save conversations in multiple formats for backup
- Prompt library: Store and access your best prompts with // shortcut
- Custom themes: Personalize ChatGPT's appearance with dark mode and color schemes
Download ChatGPT Toolbox for free and take your ChatGPT productivity to the next level with features designed for power users who manage hundreds of conversations.
Want to dive deeper into ChatGPT? Explore our related guides:

